CLOUD COMPUTING:- Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services, including storage, processing, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the Internet (the cloud). These services are provided on-demand, often on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Cloud computing enables users to access and use resources that are housed in remote data centers and managed by third parties. This means that users can access computing resources on an as-needed basis, without the need to purchase and maintain expensive hardware and software in-house.
There are several benefits to using cloud computing:
- Cost savings: Because users only pay for the resources they use, cloud computing can be more cost-effective than maintaining in-house infrastructure.
- Scalability: Cloud computing resources can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing demand, without the need to purchase additional hardware.
- Availability: Cloud computing resources are available on demand and can be accessed from anywhere with an Internet connection.
- Security: Cloud providers typically have strong security measures in place to protect user data.
There are several different types of cloud computing, including public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and community cloud. Each type has its own set of characteristics and is suited to different use cases.
Meaning of cloud computer
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services, including storage, processing, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the Internet (the cloud). These services are provided on-demand, often on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Cloud computing enables users to access and use resources that are housed in remote data centers and managed by third parties. This means that users can access computing resources on an as-needed basis, without the need to purchase and maintain expensive hardware and software in-house.
In other words, cloud computing allows users to access and use computing resources, such as storage, processing power, and software applications, over the Internet. These resources are typically provided by third-party cloud providers, who manage and maintain the underlying infrastructure. Cloud computing allows users to access and use these resources on an as-needed basis, paying only for the resources they consume. This is in contrast to traditional computing models, in which users must purchase and maintain their own hardware and software in-house.
What are cloud computers used for?
Cloud computing is used for a wide variety of applications and workloads. Some common use cases for cloud computing include:
- Data storage and backup: Cloud storage allows users to store and access data from anywhere with an Internet connection. This can be useful for storing large amounts of data, backing up important files, and sharing files with others.
- Web and mobile application development: Cloud computing allows developers to build, test, and deploy web and mobile applications more quickly and easily.
- Business applications: Many businesses use cloud computing to host their email, customer relationship management (CRM), and other business applications.
- Big data analytics: Cloud computing can be used to process and analyze large amounts of data, such as data from social media, sensors, or financial transactions.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: Cloud computing can provide the processing power and storage needed to train and deploy machine learning models.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Cloud computing can be used to manage, analyze, and act on data from connected devices in the Internet of Things.
- Disaster recovery: Cloud computing can provide a backup location for data and applications in case of a disaster.
Cloud computing can be used in a variety of other scenarios as well, depending on the specific needs of the user.
Examples of cloud computer
Here are a few examples of how cloud computing is used:
- Storing and accessing data: Dropbox is a popular example of a cloud storage service that allows users to store and access files from anywhere with an Internet connection.
- Web and mobile application development: Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure are examples of cloud platforms that provide a range of services for building, testing, and deploying web and mobile applications.
- Business applications: Google Workspace (formerly known as Google G Suite) is a cloud-based suite of productivity tools that includes email, document creation, and collaboration tools. Salesforce is a cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) platform that helps businesses manage customer interactions and data.
- Big data analytics: Hadoop is an open-source framework for storing and processing large amounts of data. It is often used in combination with cloud computing to analyze and gain insights from large datasets.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: Google Cloud Platform and AWS offer a range of tools and services for developing and deploying machine learning models.
- Internet of Things (IoT): AWS IoT is a cloud platform that allows businesses to connect, manage, and analyze data from connected devices.
- Disaster recovery: Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions, such as AWS Disaster Recovery and Microsoft Azure Site Recovery, allow businesses to replicate data and applications to the cloud for use in case of a disaster.
Types of clouds computer
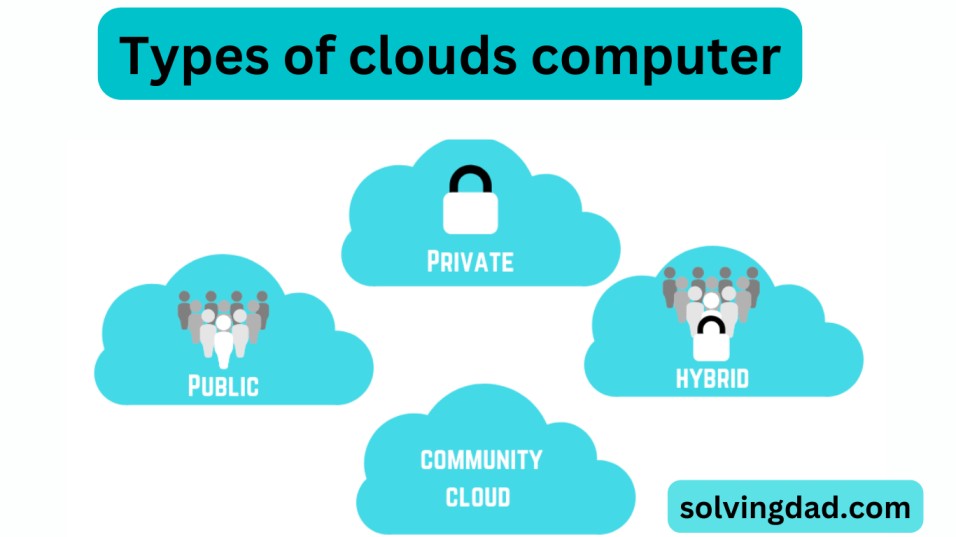
There are several different types of cloud computing, including:
- Public cloud: Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party cloud providers, who make their services available to the general public over the Internet. Examples of public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- Private cloud: Private clouds are owned and operated by a single organization and are used exclusively by that organization. Private clouds can be built and maintained in-house or by a third-party provider.
- Hybrid cloud: Hybrid clouds combine elements of both public and private clouds, allowing organizations to use a combination of on-premises and off-premises resources.
- Community cloud: Community clouds are shared by a group of organizations that have similar computing needs and are often working on similar projects.
Each type of cloud has its own set of characteristics and is suited to different use cases. For example, public clouds are typically the most cost-effective option and are well-suited for applications that have variable or unpredictable resource needs. Private clouds can provide greater control and security for organizations with specific compliance or regulatory requirements. Hybrid clouds can provide the best of both worlds, allowing organizations to take advantage of the cost-effectiveness and scalability of the public cloud while maintaining control over sensitive data in a private cloud.
What are the risks of cloud computing?
While cloud computing can offer many benefits, it also carries some risks and challenges. Some potential risks of cloud computing include:
- Security: One of the primary concerns about cloud computing is the security of data that is stored and processed in the cloud. While cloud providers generally have strong security measures in place, there is always the risk of data breaches or other security incidents.
- Compliance: Organizations that handle sensitive data, such as personal or financial information, may need to comply with specific regulations or standards. It is important to ensure that the cloud provider you choose is able to meet these requirements.
- Data loss: There is always the risk of data loss in any computing environment, including the cloud. It is important to have robust backup and recovery processes in place to minimize the risk of data loss.
- Service outages: Cloud providers may experience service outages or other disruptions that could affect the availability of your data and applications.
- Vendor lock-in: Depending on the specific cloud services and infrastructure you use, you may become reliant on a single vendor. This can create vendor lock-in, which can make it difficult or costly to switch to a different provider if you are not satisfied with the service you are receiving.
To mitigate these risks, it is important to carefully evaluate the security and compliance measures of any cloud provider you are considering, and to have robust backup and recovery processes in place. It is also a good idea to diversify your cloud resources and use a combination of different cloud providers and deployment models to reduce the risk of vendor lock-in.
Who is the father of cloud computing?
The concept of cloud computing has evolved over time, and there are several individuals and organizations that have contributed to its development.
One of the earliest proponents of the concept of cloud computing was computer scientist John McCarthy, who is often referred to as the “father of artificial intelligence.” In the 1960s, McCarthy proposed the idea of a “galactic network” of computers that could be accessed and used by anyone, anywhere.
In the late 1990s and early 2000s, a number of companies and organizations played a key role in the development and popularization of cloud computing. These include:
- Salesforce: Salesforce introduced the concept of Software as a Service (SaaS), in which software applications are delivered over the Internet on a subscription basis.
- Amazon: In 2002, Amazon introduced its Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), which allowed users to rent computing resources on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- Google: In 2006, Google launched Google App Engine, which allowed developers to build and host web applications on Google’s infrastructure.
- Microsoft: In 2010, Microsoft launched Windows Azure, a cloud platform that provides a range of services for building, deploying, and managing applications and data.
While it is difficult to identify a single “father of cloud computing,” these and other individuals and organizations have contributed significantly to the development and evolution of the field.
Layers of cloud computing
There are several layers to cloud computing, including:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This layer provides the underlying infrastructure required to support cloud computing, including physical servers, storage, and networking.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): This layer provides a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications, including tools, frameworks, and middleware.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): This layer provides access to software applications that are delivered over the Internet and accessed through a web browser.
- Data as a Service (DaaS): This layer provides access to data and analytics tools, such as data warehouses and business intelligence software.
- Function as a Service (FaaS): This layer provides access to serverless computing, which allows developers to run code in response to specific events or triggers.
Each layer builds on the one below it, and together, they form the foundation of cloud computing. These layers are often referred to as the “cloud computing stack,” and they can be used in combination to create a variety of cloud-based solutions.
Basic Components of Cloud Computing
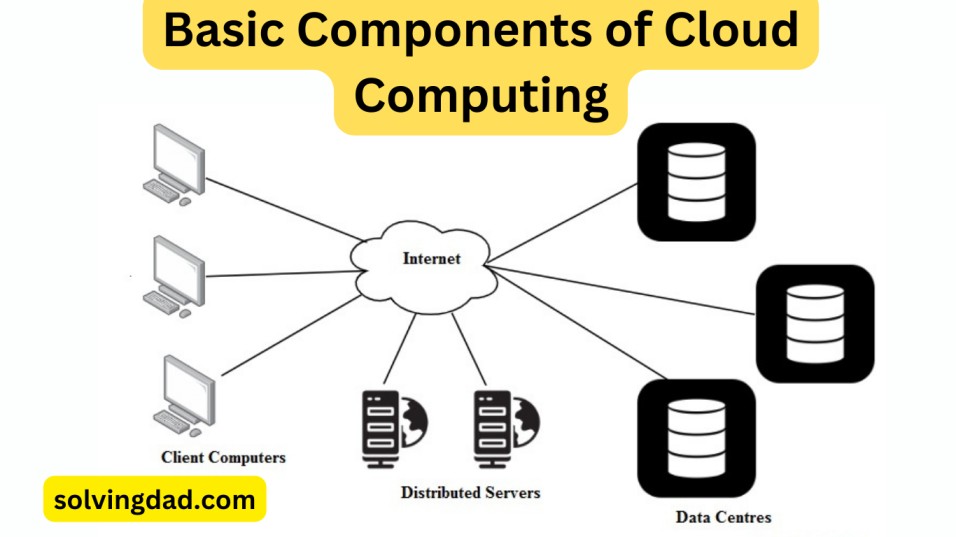
There are several basic components of cloud computing, including:
- Client devices: These are the devices that users use to access cloud services, such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
- Network: A network, such as the Internet, is used to connect client devices to the cloud.
- Cloud servers: These are the servers that provide the computing resources and storage for cloud services.
- Cloud storage: This is the storage that is used to store data and files in the cloud.
- Cloud software: This is the software that is used to manage and coordinate the various components of the cloud, including the cloud servers and storage.
- Cloud applications: These are the applications that users access and use in the cloud, such as email, productivity tools, and customer relationship management (CRM) software.
Together, these components form the infrastructure of a cloud computing system, which allows users to access and use computing resources over the Internet on an as-needed basis.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
There are several characteristics that define cloud computing, including:
- On-demand self-service: Cloud computing allows users to access and use computing resources on an as-needed basis, without the need for human intervention.
- Broad network access: Cloud computing resources can be accessed over the Internet from a variety of devices, including laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
- Resource pooling: Cloud providers pool resources, such as storage and processing power, and allocate them to users as needed.
- Rapid elasticity: Cloud computing resources can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing demand.
- Measured service: Cloud providers typically track and measure resource usage, allowing users to pay only for the resources they consume.
These characteristics make cloud computing a flexible and cost-effective way for organizations and individuals to access and use computing resources.
Conclusion:-
In conclusion, cloud computing is a model of delivering computing services, including storage, processing, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the Internet. It enables users to access and use resources that are housed in remote data centers and managed by third parties, on an as-needed basis, without the need to purchase and maintain expensive hardware and software in-house.
There are several different types of cloud computing, including public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and community cloud, and each type is suited to different use cases. Cloud computing has many benefits, including cost savings, scalability, availability, and security, but it also carries some risks and challenges, including security, compliance, data loss, service outages, and vendor lock-in. To mitigate these risks, it is important to carefully evaluate the security and compliance measures of any cloud provider you are considering, and to have robust backup and recovery processes in place.
