The computer is made up of various parts. These components or devices enable it to function. There are various types of components, which are listed below. I have explained all components of the computer individually. The Components of the Computer are:-
The Outside of a Computer
When you look at your computer, what you see is actually the computer case. Inside these cases are all of the individual factors that when connected together produce your computer. On the outside of the case, you’ll see colorful external anchorages that you can plug bias into as well as the capability to pierce your optic bias similar to your CD and DVD drives.

On the front of the computer, you’ll generally find a CD or DVD drive that can be opened by pressing a small button near the door of the drive. This will eject the drive charger where you can place a CD or DVD fragment. When you press the button again, the charger will slide back into your computer so that you can pierce it from within your operating system. On the front of the case, you’ll also generally find USB anchorages and media compendiums. A USB harborage is a small opening on the front of your computer that allows you to plug a USB device harborage is a small opening on the front of your computer that allows you to plug a USB device or string into it.
Back Panel
You can generally determine if a harborage on your computer is USB as it’ll have the totem next to it. The common bias that you would plug into USB anchorages is iPods and iPads, flash drives, and external hard drives. The other common anchorages that you can find are for camera memory media. These media compendiums allow you to remove the memory card from your camera and fit it into the computer so you can pierce the images stored on it.

On the reverse of the case are connectors that are generally only used when you assemble your computer for the first time. These connectors allow you to connect external bias similar as your printer, examiner, mouse, keyboard, and speaker. The reverse connections will also include an Ethernet harborage that will allow you to connect your computer to your network. Last, but not least, there will also be more USB anchorages available in the event that you need further USB connections than are available on the front of the computer.
The Inside of the Computer
Inside the Computer, there is a lot of corridor performing corridor are available. Once you can see inside a computer, you’ll see colorful individual factors connected via lines or plugged directly into a large board attached to the side of the case. This board is the motherboard and is used to connect all the individual biases inside your case to a single computer. There are colorful factors connected to each other. Every component inside the computer is connected to each other. Every device must be connected to the powerful force unit, which provides electricity to colorful factors.

The add-on cards, each performing their own function, are fitted into the motherboard so that they can communicate with it. When all of these factors are duly connected to each other, they can also communicate with each other and the computer will operate duly. In the coming section, we will bandy each individual element and what function they serve.
Components of Computer
Let us discuss the individual components and the function that each performs in the Computer.
Computer Case
Computer cases come in different sizes and shapes in order to accommodate the colorful surroundings in which they will be stored. These shapes and sizes are:
- Tower: A tower case is perpendicular and generally sits on the bottom. A Tower case comes in mini, medial, and full sizes, with larger sizes holding further factors.
- Desktop: A desktop case that’s designed to rest on a shelf or sit in your office with the examiner on top of it.
- Rackmount: Rackmount cases are vertical and are generally used by waiters. These waiters will also mount in a rack so that there are heaps of computers in one computer rack.
Computer cases also need to support the largest element that resides inside it, which is generally the motherboard. The motherboard can come in numerous different shapes and sizes, called form factors, and the specifications of a computer case will state which form factors can fit inside it.

All modern cases have these functionalities:
- Power switch.
- Modern Cases have Indicator lights on the front of the case like disk activity, network activity, etc.
- The back panel contains holes to expose external ports.
- Mounting points to allow secure the motherboard.
- Vented panels allow airflow through the case.
Depending on the model, some cases have other features as well similar to headphone jacks or USB anchorages.
Motherboard
The Motherboard is the most functioning part of the computer that connects all components of the computer with each other. It’s a fairly large, blockish, board filled with colorful circuits, vessels, and places that you plug effects into the motherboard serves two functions. First, the motherboard is home to a number of chips, that mandate how the colorful factors of the computer will talk to each other.
It also has special places that allow you to plug expansion cards in that add new or advanced functionality to your computer. Secondly and maybe most importantly, the motherboard is the connecting point for all of the other pieces of the computer. Without the motherboard, the different corridors can not communicate with each other and the computer can not serve. This is the main component of the Computer, It connects all parts of the computer with each other.

Motherboards connect with the other bias in your computer using a set of special places and connectors called anchorages that are located on the top and aft edge of the motherboard. The anchorages on the aft edge of the motherboard bag out of the aft panel of the computer case allow you to connect external bias to the computer. nearly all ultramodern motherboards have one or further USB anchorages and an Ethernet harborage mounted externally to allow connection to the internet and external bias. also, all ultramodern motherboards contain at least one IDE or SATA harborage to allow the connection of a hard drive.
System Bus
A machine is generally a collection of cables that is responsible for hitching the colorful factors of a microcomputer together in order to allow the exchange of data between these factors and to give power to them. System Bus Types and Functions.

The CPU moves data around the computer on pathways that connect it to all the other factors on the motherboard. These pathways are called’ motorcars’. The internal machine carries data within the motherboard. External motorcars carry data to peripherals and other biases attached to the motherboard. The lines or legs of a machine are of three types:
- Address – The factors pass memory addresses to one another over the address machine.
- Control – Used to shoot out signals to coordinate and manage the conditioning of the motherboard factors.
- Data – Transferred between peripherals memory and the CPU. Obviously, the data machine can be a veritably busy pathway.
BIOS
Memoirs are known as introductory Input/ Affair Systems an electronic set of instructions that a computer use to successfully start operating. The memoirs are located on a chip inside of the computer and are designed in a way that it from fragment failure. The main function of the memoirs is to give instructions for the power- on tone test( POST). This tone test ensures that the computer has all of the necessary corridors and functionality demanded to successfully start itself, similar to the use of memory, a keyboard, and other corridors.

still, the BIOS instructs the computer to five a law that reveals the problem, If errors are detected during the test. Error canons are generally a series of beeps heard shortly after incipiency. The BIOS also works to give the computer introductory information about how to interact with some critical factors, similar to drives and memory, that it’ll need to load the operating system. Once the introductory instructions have been loaded and the tone-tested has been passed, the computer can do with loading the operating system from one of the attached drives.
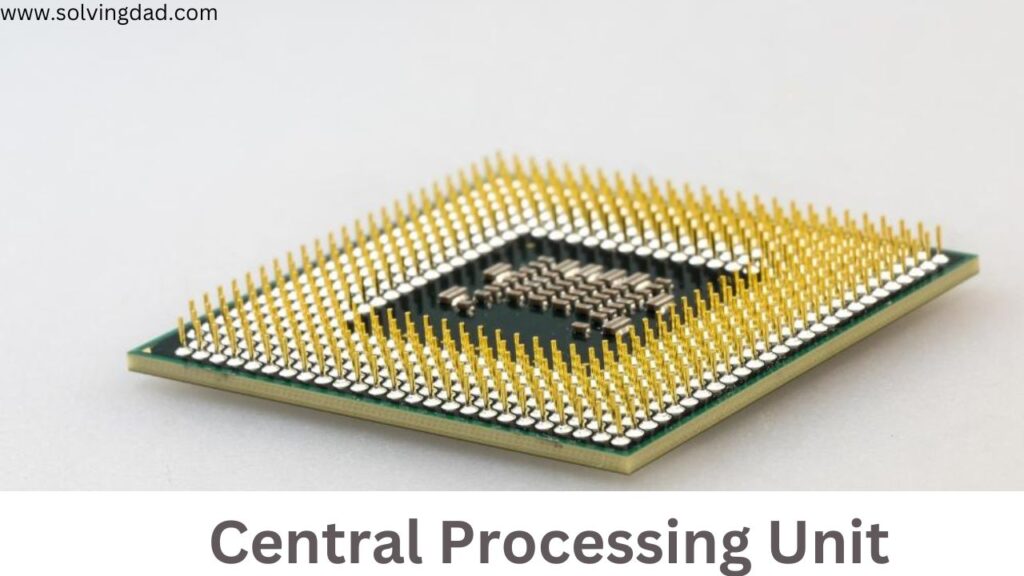
Central Processing Unit
The Central Processing Unit is popularly known as the CPU or Processor, it is the brain o the computer. The CPU is located on the motherboard and is connected to it through a special harborage called the CPU socket. When the CPU is in use it generates heat, which must be transferred down from the CPU chip so that it isn’t damaged. This is fulfilled through the use of a heat Gomorrah and addict which draws the heat out of the CPU chip and transfers it into the case rather.
The processor is known by the other name CPU. It’s that part that substantially drives the computer. A processor interprets instructions given to the computer and executes them. This is one of the most important components of the computer. It’s a small element nearly 3 cm x 3 cm in confines. It’s connected to the motherboard and an addict is fixed over it to cover it from heating when the computer is ON.
According to the functions of the Central Processing Unit, processors are of the following types:
Single-Processors:- A system that has only one central processing unit. This processor is fairly slow for a high volume of data.
Dual-Processors:- The system which has two or further processors but only one processor is busy at a time for its operations. When one CPU is busy, the other is idle. When one is idle, the other becomes active automatically.
Multi-Processor:- Multiple processors is a connection of two or further CPUs. Some motherboards are so circumvented that they could accommodate two or further processors on them. They partake in the cargo and work with full effectiveness.
Power Supply Unit
All corridors of a computer bear electricity in order to operate. The part of the computer that provides this electricity is called the power force unit or PSU. The PSU receives electricity from an external source, which is generally a wall outlet, and changes it into power that the other corridor of the computer can use. A PSU is necessary for two reasons. First, computers bear direct current, or DC, power. still, electricity is supplied by power companies in interspersing current, or AC, form.

The PSU takes the AC electricity and converts it into a DC form so that the computer factors use the electrical power of fairly low voltage, while the electricity that comes out of a wall socket is of a significantly advanced voltage form that the computer can duly use.
Hard Disk Drive
The hard fragment drive or HDD is the primary source of secondary storehouse in ultramodern computers. A secondary storehouse is any device where information is stored when it isn’t demanded immediate use. An HDD uses captivation to record information on a rotating fragment of glamorous material. It uses a portable arm containing a device called a drive head to read from and write to different portions of the fragment. Since the fragment remains bewitched indeed after power is removed, information isn’t lost when you turn off the computer. One strike of HDDs is that they’re veritably slow compared to other biases in the computer. This is because the motorist must place the arm and fragment in the correct position in order to recoup a particular piece of information.

ultramodern HDDs have three major variables. The first is the drive capacity. This is how important information the drive can hold. Drive capacity is measured in either gigabytes or terabytes. The alternate variable is the gyration speed. This is how snappily the fragment inside the HDD can rotate and is measured in reels per nanosecond. The briskly the fragment spins, the more snappily information can be recaptured from it The final variable is the type of interface the HDD uses. Utmost ultramodern HDDs use SATA or SAS interfaces, although HDDs using IDE interfaces are still kindly
common.
Optical Disk Drives
An optic fragment drive is an element that uses a ray to read from or write to an optic fragment. exemplification of optic disks includes CDs, DVDs, and Blu- shafts. An optic fragment drive writes to a fragment by using a ray to etch bitsy grooves into the face of the fragment. The fragment is read by using a different, low-power ray to descry those grooves ultramodern optic fragment drives generally have reading and jotting capabilities. also, utmost optic drives are backward compatible, which means that new technology can read the media from an aged technology. For illustration, a Blu- Ray drive can also play DVDs and CDs.

Optic fragment drive speed is measured else than HDD speed. Optic drive speed is measured by the maximum rate at which data can be read from the fragment. For each technology, there’s an assiduity-wide standard data rate that serves as a standard by which drive pets are measured. The speed listed is put in terms of multiples of that base speed. For illustration, the base speed for Blu- Ray technology is6.74 megabytes per second. thus, a drive rated at 52x can read data at a maximum rate of 52 x6.74 = 350.48 megabytes per second.
Cooling Devices
The computer generates a lot of heat when it’s working. One or further cooling biases are part of any ultramodern computer in order to keep the machine from overheating. The two types of cooling bias that is in nearly every ultramodern computer are heat cesspools and cooling suckers. heat cesspools are small essence structures that conduct heat well. They serve by absorbing the heat produced by an element and efficiently releasing it into the air or a liquid in certain special situations, analogous to how the radiator in your auto works.

Cooling devices work by removing warm air from factors or heat cesspools and pulling by cool air to replace it. suckers are available in a variety of sizes that determine how important air they can move within your case. When adding an addict, it’s important to insure that you buy an addict that’s compatible with your motherboard, since different suckers have different kinds of power connections.
Memory
Random Access Memory or RAM is the part of the computer where information is stored while it’s being used by the computer’s processor, operating system, programs, and other biases on your computer, RAM is designed so that any of your information stored on it can be read in any order without losing performance. This makes RAM brisk and more effective to store data compared to slower bias similar as an HDD or CD- ROM.

When you’re using your computer it clones information that it’s presently using, similar to a corridor of the operating system or presently running programs, into RAM so that it can work the important slower HDD. To use a comparison, suppose your HDD is as well. The information on the HDD is the water in the well and the RAM is a pail. The bigger your pail, the smaller passages you have to make to the well to get the water you need. One specific of RAM is that it’s unpredictable. This means that when you turn off the computer, any information in the RAM is canceled. To cover against loss of information, an operating system will copy any data that it needs to the HDD so that it’s available at the coming time you start the computer.
RAM comes in different pets and types. When you upgrade your computer’s memory. It’s important to insure that you choose a speed and type of RAM that’s compatible with a computer’s motherboard.
Expansion Cards
An expansion card is a device that’s fitted into special places on the motherboard and provides the computer with fresh functions, coffers, or features. There are a number of different kinds of expansion cards available, two of the most common being videotape cards, which give increased plate recycling capability, and sound cards, which enhance the audio capability of the computer. Some expansion cards similar to videotape cards also include their own processor, memory, and indeed cooling bias similar as suckers or heat cesspools.

When copping expansion cards there are a number of important factors to consider. First and foremost is the type of connection that the expansion card requires. There are a number of different norms for expansion places and motherboards have only a limited number of each kind of niche. Before copping
you need to insure that your motherboard has the needed places available to use. Another important factor is the size of the expansion card. The card needs to be suitable to fit inside your computer case and shouldn’t make contact with any other corridor of the computer except for the motherboard.
Eventually, you should insure that your PSU can affair enough power to support all your connected expansion cards. If the PSU can not supply the computer with enough electricity also one or further of your bias will fail to serve. Two common types of expansion cards are sound and video plate cards.
Sound Cards

Sound cards are a kind of expansion card that deals with audio input and affairs. They generally fill two functions. First, sound cards enhance the sound processing capability of the computer, allowing for the creation and affair of further complex sounds. Secondly, sound cards frequently retain input and affair anchorages that allow for other audio bias similar to microphones or speakers to be connected to them.
Video Cards
A videotape card is a type of expansion card that increases the computer’s capability to handle different kinds of visual affairs. videotape cards have two main functions. First, while nearly all ultramodern motherboards have some introductory plate capabilities erected in, a videotape card can handle plate issues much more effectively than the graphic chips erected into the motherboard.
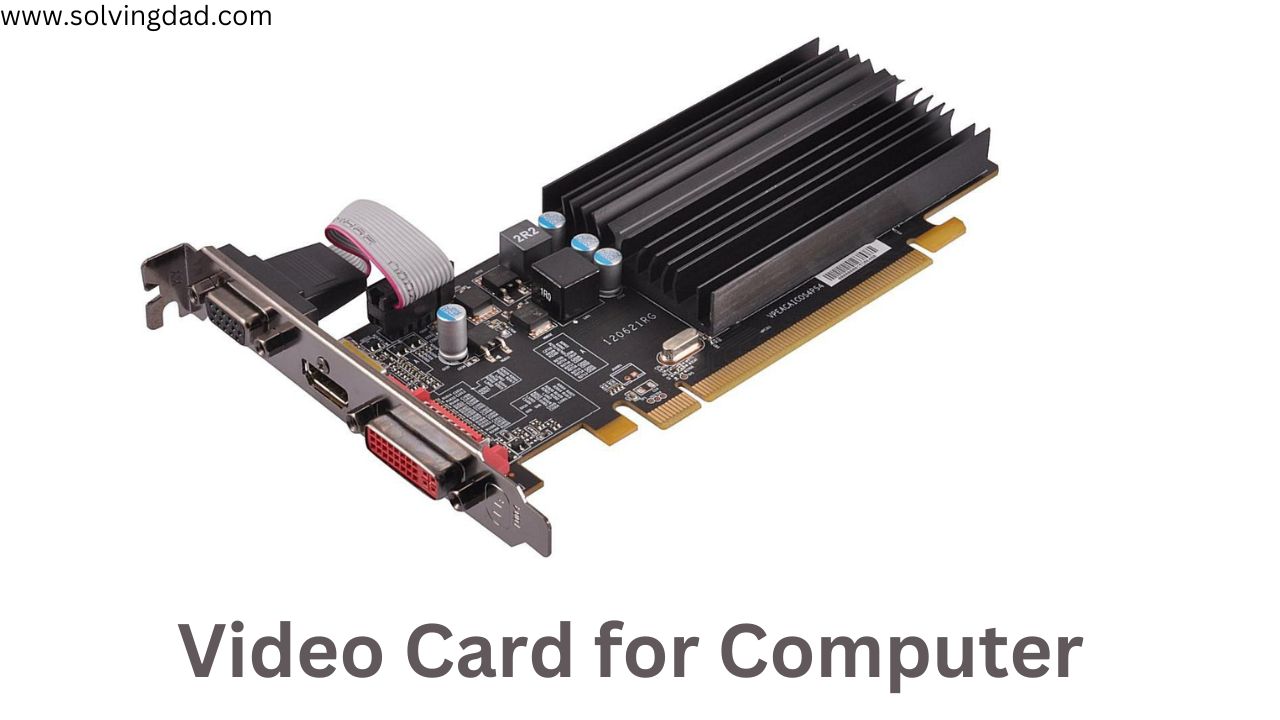

As a result, a videotape card allows for the creation and display of more complex and detailed images without putting a fresh strain on the CPU. also, since numerous videotape cards have their own memory, this leaves further the general computer memory available for other purposes. Second, numerous videotape cards add fresh functions to the computer similar to videotape prisoner, a television tuner that allows you to watch television on your computer, or the capability to connect multiple observers to the computer.
External Ports
As mentioned in the motherboard section, a number of connectors on the motherboard are accessible from the computer case’s back panel. External ports are so-called because they can be accessed from outside the computer case. There are several different types of connections available, including:
- VGA or DVI Connector: You can connect a monitor or other display device to your computer using these ports.
- Ethernet Port – This port allows you to connect your computer to a network or the Internet.
- HDMI – This port allows you to connect your computer or laptop to Another screen or TV.
- eSATA – This port allows you to connect an external hard to your computer which supports SATA cable.
- USB Port – A standard connector for connecting external devices. More information on USB ports can be found further down.
Almost all modern PCs also have one or more USB or Universal Serial Bus ports. There are two main types of USB connectors in use today: USB 2.0 and USB 3.0. USB 3.0 ports can transfer data much faster than USB 2.0 ports. However, the attached device must be designed to take advantage of USB 3.0 technology to take advantage of the increased speeds.

USB ports and devices are backward and forward-compatible. This means that you can plug a standard USB device into a standard USB port and it will work. However, if the USB versions of the device and part do not match, the device can only transfer data to and from the PC at the maximum speed determined by the lower of the two versions. For example, if you plug a USB 3.0 device into a USB 2.0 port, the device will only transfer data at its maximum speed of 60 megabytes per second, the maximum speed of USB 2.0 technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most important Computer Component?
The motherboard is the most important Components of Computer.
How many Components are in a Computer?
There are many components in a Computer but there are three main components in a computer Monitor, Input/Output Devices, and Cabinet (including Central Processing Unit, RAM, Hard Disk, and Motherboard). These are the essential components of a computer that are required to start a computer.
Which is bigger KB or GB?
GB is bigger than KB
1024 Kb = 1 Mb
1024 Mb = 1 Gb
What goes after TB
Petabyte comes after TB (terabyte)
Conclusion
These are the components of the computer which I have explained individually. You will find each and everything about the components of a Computer. A Computer needs some basic devices to start like Motherboard, RAM, Hard Disk, CPU, Monitor, and I/O Devices. I hope this information will very useful for you and will add some value to your life.
Thanks for visiting our website solvingdad.com